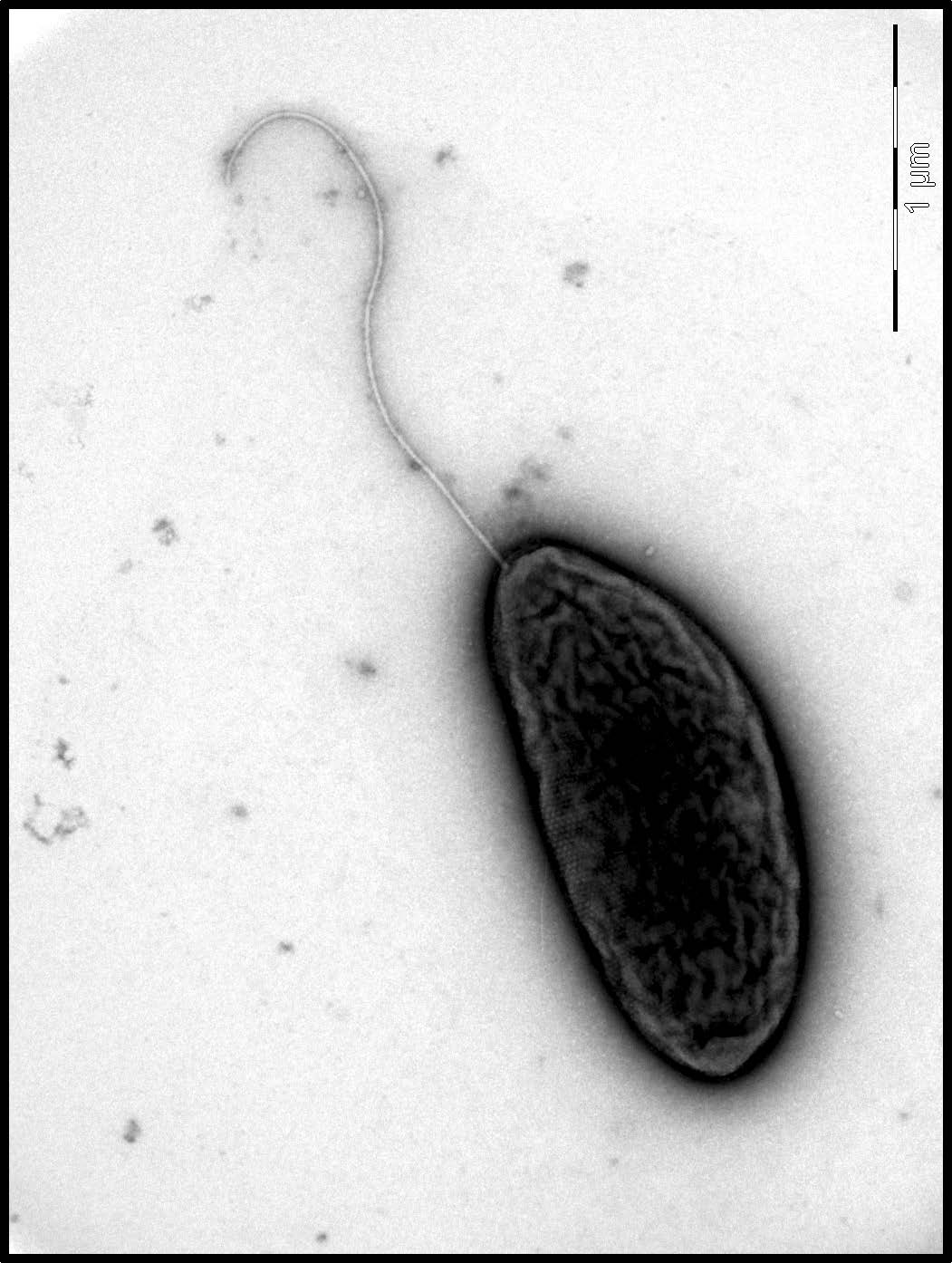
Sialic acids are 9-carbon keto sugars involved in a wide range of functions across all branches of life
Sialic acids are 9-carbon keto sugars involved in a wide range of functions across all branches of life. Bacteria are able to biosynthesize them and incorporate them into cell-surface structures to regulate motility, biofilm formation, and host immune avoidance. Bacteria are careful to select the correct surface protein or molecule and add the correct sialic acid to it. Nucleotide-activated sialic acids commonly serve as glycosyl donors, particularly pseudaminic acid (Pse) and its stereoisomer legionaminic acid (Leg), which can be used to decorate bacterial flagella. FlmG, a recently identified protein sialyltransferase, O-glycosylates flagellins, the subunits of the flagellar filament in bacteria.The group of Patrick Viollier showed that flagellin glycosylation and motility in Caulobacter crescentus and Brevundimonas subvibrioides is conferred by functionally insulated Pse and Leg biosynthesis pathways, respectively, and by a Pse- or Leg-specific FlmG ortholog, respectively. They established a genetic glyco-profiling platform for the classification of Pse or Leg biosynthesis pathways and they reprogrammed FlmG glycosylation with Leg using chimeric FlmG proteins.