« Back to all publications
Download this list in a RIS file or a BIB file or a PDF file
|
 |
|||||||
Whereas the photoinduced charge-transfer properties of electron donor–acceptor dyads are now well understood, those of symmetric conjugated architectures containing several identical donor–acceptor branches have started to be scrutinised much more recently. Here, we report on our investigation of the charge-transfer dynamics of a series of formally centrosymmetric triads consisting of a quadrupolar dihydropyrrolopyrrole core substituted with two identical diphenylethynyl lateral branches. Using a combination of time-resolved electronic and vibrational spectroscopies, we show that these molecules exhibit rich excited-state dynamics, which includes three different types of symmetry-breaking charge-transfer processes depending on the nature of the end substituents on the core and branches as well as on the solvent: (i) excited-state symmetry breaking within the core; (ii) charge transfer from the core to one of the two branches; (iii) charge transfer between the two branches. This investigation illustrates how the excited-state properties of symmetric conjugated molecules, including the nature and location of the exciton, can be controlled by fine tuning structural as well as environmental parameters. | ||||||||
 |
|
|||||||
Electronic excitation in quadrupolar conjugated molecules rapidly localizes on a single electron donor–acceptor (DA) branch when in polar environments. The loss of center of inversion upon this excited-state symmetry breaking (ES-SB) can be monitored by exploiting the relaxation of the exclusion rules for IR and Raman vibrational transitions. Here, we compare ES-SB in a right-angled (1) and a centrosymmetric (2) DAD dyes using time-resolved IR spectroscopy. We show that the localization of the excitation can also be identified with the bent molecule 1. We find that contrary to dye 2, subpopulations with localized and delocalized excitation coexist for 1 in weak to medium polar solvents. This difference originates from the torsional disorder present in the excited state of 1 but not of 2. Additionally, irreversible localization in a bent molecule is shown to require higher solvent polarity than in a centrosymmetric one. | ||||||||
|
 |
|||||||
The torsional disorder of conjugated dyes in the electronic ground state can lead to inhomogeneous broadening of the S1 â†S0 absorption band, allowing for the selective photoexcitation of molecules with different amounts of distortion. Here, we investigate how this affects electronic transitions to upper excited states. We show that torsion of a core-alkynylated push–pull dye can have opposite effects on the oscillator strength of its lowest-energy transitions. Consequently, photoselection of planar and twisted molecules can be achieved by exciting in distinct absorption bands. Whereas this has limited effect in liquids due to fast planarization of the excited molecules, it strongly affects the overall photophysics in a polymeric environment, where torsional motion is hindered, allowing for the photoselection of molecules with different fluorescence quantum yields and intersystem-crossing dynamics. | ||||||||
 |
|
|||||||
Fluorescent flippers have been introduced as small-molecule probes to image membrane tension in living systems. This study describes the design, synthesis, spectroscopic and imaging properties of flippers that are elongated by one and two alkynes inserted between the push and the pull dithienothiophene domains. The resulting mechanophores combine characteristics of flippers, reporting on physical compression in the ground state, and molecular rotors, reporting on torsional motion in the excited state, to take their photophysics to new level of sophistication. Intensity ratios in broadened excitation bands from differently twisted conformers of core-alkynylated flippers thus report on mechanical compression. Lifetime boosts from ultrafast excited-state planarization and lifetime drops from competitive intersystem crossing into triplet states report on viscosity. In standard lipid bilayer membranes, core-alkynylated flippers are too long for one leaflet and tilt or extend into disordered interleaflet space, which preserves rotor-like torsional disorder and thus weak, blue-shifted fluorescence. Flipper-like planarization occurs only in highly ordered membranes of matching leaflet thickness, where they light up and selectively report on these thick membranes with red-shifted, sharpened excitation maxima, high intensity and long lifetime. | ||||||||
|
 |
|||||||
The inclusion of boron atoms into chiral À-conjugated systems is an effective strategy to unlock unique chiroptical properties. Herein, the preparation and characterization of a configurationally stable axially-chiral boramidine are reported, showcasing absorption in the UV domain, deep-blue fluorescence ( up to 94%), and ca. |10-3| g_abs and g_lum values. Detailed photophysical studies and quantum-chemical calculations clearly elucidate the deactivation pathways of the emissive state to triplet excited states, involving increased spin–orbit coupling between the lowest singlet excited state and an upper triplet state. | ||||||||
 |
|
|||||||
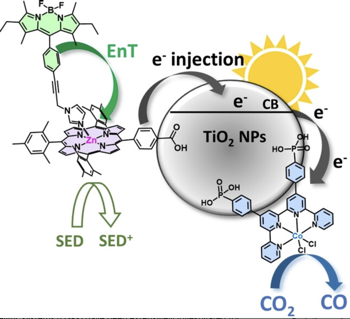
Dye-sensitized photocatalytic systems (DSPs) have been extensively investigated for solar-driven hydrogen (H2) evolution. However, their application in carbon dioxide (CO2) reduction remains limited. Furthermore, current solar-driven CO2-to-CO DSPs typically employ rhenium complexes as catalysts. In this study, we have developed DSPs that incorporate noble metal-free components, specifically a zinc-porphyrin as photosensitizer (PS) and a cobalt-quaterpyridine as catalyst (CAT). Taking a significant stride forward, we have achieved an antenna effect for the first time in CO2-to-CO DSPs by introducing a Bodipy as an additional chromophore to enhance light harvesting efficiency. The energy transfer from Bodipy to zinc porphyrin resulted in remarkable stability (turn over number (TON)=759 vs. CAT), and high CO evolution activity (42?mmol?g?1?h?1 vs. CAT). | ||||||||
|
 |
|||||||
So far, symmetry-breaking charge separation (SB-CS) has been observed with a limited number of chromophores and is usually inhibited by the formation of an excimer. We show here that thanks to fine-tuning of the interchromophore coupling via structural control, SB-CS can be operative with pyrene, despite its high propensity to form an excimer. This is realized with a bichromophoric system consisting of two pyrenes attached to a crown ether macrocycle, which can bind cations of different sizes. By combining stationary and time-resolved spectroscopy together with molecular dynamics simulations, we demonstrate that the excited-state dynamics can be totally changed depending on the binding cation. Whereas strong coupling leads to rapid excimer formation, too weak coupling results in noninteracting chromophores. However, intermediate coupling, achieved upon binding of Mg2+, allows for SB-CS to be operative. | ||||||||
 |
|
|||||||
There is a growing interest in developing dye-sensitized photocatalytic systems (DSPs) to produce molecular hydrogen (H2) as alternative energy source. To improve the sustainability of this technology, we replaced the sacrificial electron donor (SED), typically an expensive and polluting chemical, with an alcohol oxidation catalyst. This study demonstrates the first dye-sensitized system using a diketopyrrolopyrrole dye covalently linked to 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidine-N-oxyl (TEMPO) based catalyst for simultaneous H2 evolution and alcohol-to-aldehyde transformation operating in water with visible irradiation. | ||||||||
|
 |
|||||||
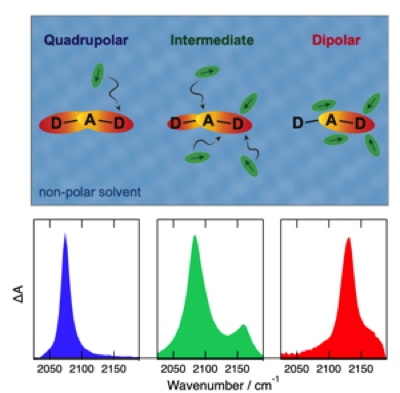
A large number of multipolar dyes undergo excited-state symmetry breaking (ESSB) in polar media. During this process, electronic excitation, initially distributed evenly over the molecule, localizes, at least partially, on one donor–acceptor branch. To resolve its initial stage, ESSB is investigated with a donor–acceptor–donor dye in binary mixtures of nonpolar and polar solvents using time-resolved infrared absorption spectroscopy. The presence of a few polar molecules around the dye is sufficient to initiate ESSB. Although the extent of asymmetry in a mixture is close to that in a pure solvent of similar polarity, the dynamics are slower and involve translational diffusion. However, preferential solvation in the mixtures leads to a larger local polarity. Furthermore, inhomogeneous broadening of the S1 <- S0 absorption band of the dye is observed in the mixtures, allowing for a photoselection of solutes with different local environments and ESSB dynamics. | ||||||||
 |
|
|||||||
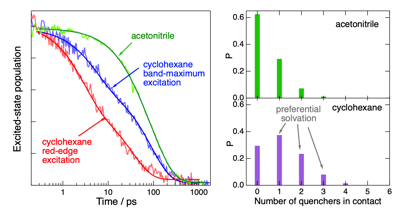
Electron transfer (ET) quenching in nonpolar media is not as well understood as in polar environments. Here, we investigate the effect of dipole–dipole interactions between the reactants using ultrafast broadband electronic spectroscopy combined with molecular dynamics simulations. We find that the quenching of the S1 state of two polar dyes, coumarin 152a and Nile red, by the polar N,N-dimethylaniline (DMA) in cyclohexane is faster by a factor up to 3 when exciting on the red edge rather than at the maximum of their S1 ↠S0 absorption band. This originates from the inhomogeneous broadening of the band due to a distribution of the number of quencher molecules around the dyes. As a consequence, red-edge excitation photoselects dyes in a DMA-rich environment. Such broadening is not present in acetonitrile, and no excitation wavelength dependence of the ET dynamics is observed. The quenching of both dyes is markedly faster in nonpolar than polar solvents, independently of the excitation wavelength. According to molecular dynamics simulations, this is due to the preferential solvation of the dyes by DMA in cyclohexane. The opposite preferential solvation is predicted in acetonitrile. Consequently, close contact between the reactants in acetonitrile requires partial desolvation. By contrast, the recombination of the quenching product is slower in nonpolar than in polar solvents and exhibits much smaller dependence, if any, on the excitation wavelength. | ||||||||
|
 |
|||||||
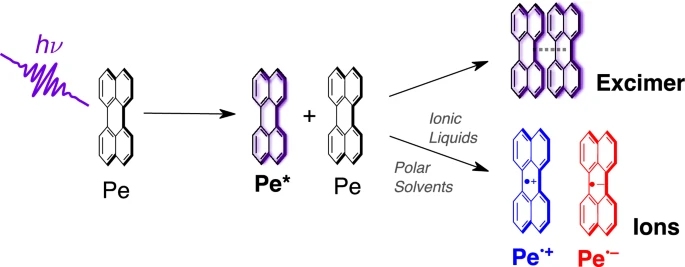
Photoinduced symmetry-breaking charge separation (SB-CS) results in the generation of charge carriers through electron transfer between two identical molecules, after photoexcitation of one of them. It is usually studied in systems where the two reacting moieties are covalently linked. Examples of photoinduced bimolecular SB-CS with organic molecules yielding free ions remain scarce due to solubility or aggregation issues at the high concentrations needed to study this diffusion-assisted process. Here we investigate the excited-state dynamics of perylene (Pe) at high concentrations in solvents of varying polarity. Transient absorption spectroscopy on the subnanosecond to microsecond timescales reveal that self-quenching of Pe in the lowest singlet excited state leads to excimer formation in all solvents used. Additionally, bimolecular SB-CS, resulting in the generation of free ions, occurs concurrently to excimer formation in polar media, with a relative efficiency that increases with the polarity of the solvent. Moreover, we show that SB-CS is most efficient in room-temperature ionic liquids due to a charge-shielding effect leading to a larger escape of ions and due to the high viscosity that disfavours excimer formation. | ||||||||
|
||||||||
Understanding the origin of electron-phonon coupling in lead halide perovskites is key to interpreting and leveraging their optical and electronic properties. Here we show that photoexcitation drives a reduction of the lead-halide-lead bond angles, a result of deformation potential coupling to low-energy optical phonons. We accomplish this by performing femtosecond-resolved, optical-pump-electron-diffraction-probe measurements to quantify the lattice reorganization occurring as a result of photoexcitation in nanocrystals of FAPbBr(3). Our results indicate a stronger coupling in FAPbBr(3) than CsPbBr(3). We attribute the enhanced coupling in FAPbBr(3) to its disordered crystal structure, which persists down to cryogenic temperatures. We find the reorganizations induced by each exciton in a multi-excitonic state constructively interfere, giving rise to a coupling strength that scales quadratically with the exciton number. This superlinear scaling induces phonon-mediated attractive interactions between excitations in lead halide perovskites. | ||||||||
Download this list in a RIS file or a BIB file or a PDF file
Contact:
Eric Vauthey
Physical Chemistry Department - Sciences II - University of Geneva
30, Quai Ernest Ansermet - CH-1211 Geneva 4 (Switzerland)
© All rights reserved by Eric Vauthey and the University of Geneva
Design and code by Guillaume Duvanel