Recherches (en anglais)
Research in the Lacour group aims at the preparation of chiral salts and ylides, and their use in synthetic (asymmetric) chemistry in a broad sense.
More
An emphasis is given to the preparation and characterization of new – usually chiral – molecular structures using unprecedented chemical transformations or mechanistic pathways. Strategies are developed to prepare these often-elaborate skeletons from simple building blocks in very few synthetic steps – possibly only one. This is rendered feasible by the combined use of high-energy intermediates (anions, cations, carbenes, nitrenes) and metal catalysis for selectivity and kinetics. Finally, with the new compounds in hand, properties are carefully analyzed and, whenever possible, applied to a variety of topics and fields.
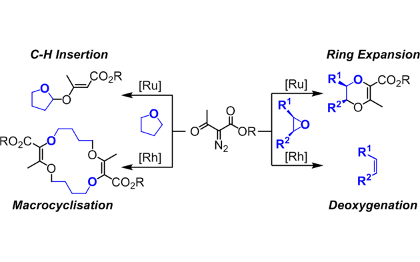
Reactive carbenes and resulting ylide chemistry
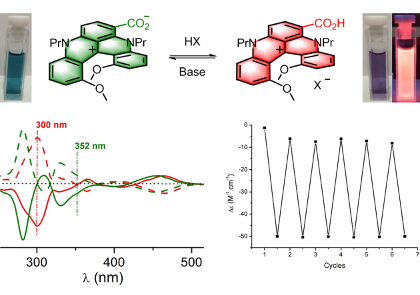
Our group is interested in the chemical structure and reactivity of oxonium, ammonium and carbonyl ylides in particular.
More
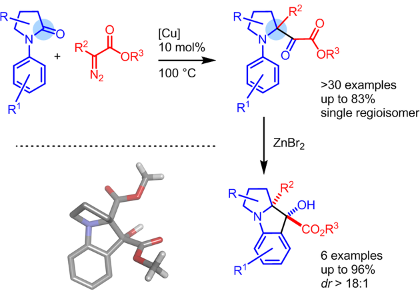
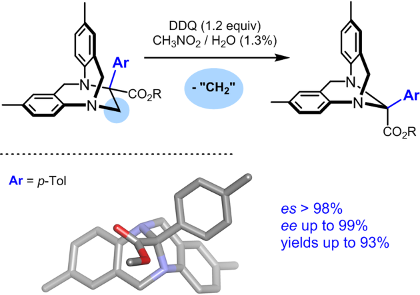
Carbenes are electrically neutral low-valent forms of carbon that are highly reactive when substituted with strong electron-withdrawing groups. These electrophilic species react well with Lewis bases to generate ylide intermediates. Our group is interested in the chemical structure and reactivity of oxonium, ammonium and carbonyl ylides in particular. A large array of original transformations and structures are generated in a single step – and heterocycles in particular.
For recent or key references, see publications: 179, 178, 177, 169, 168, 166, 164, 163, 159, 157, 152, 150, 137, 136, 130, 128, 127, 124.
Cationic Helicenes and related derivatives
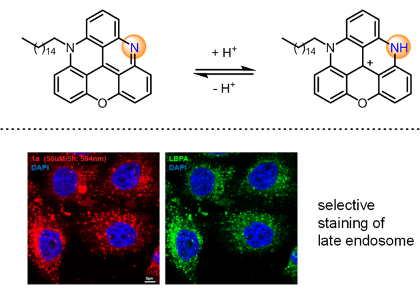
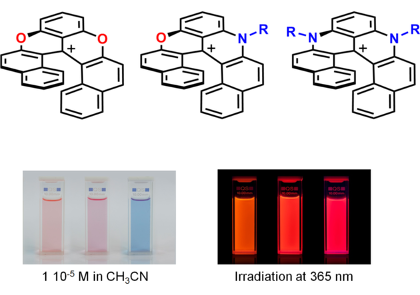
Our group develops short & highly modular syntheses of functionalized triangulenes, [4]helicenes and [6]helicenes and study applications – from Biology to Physics.
More
Triaryl-substituted carbenium ions (carbocations) are important building blocks, readily prepared from simple precursors and presenting a large panel of tunable geometrical, chemical and physical properties. Our group develops syntheses (short, highly modular) and the use of functionalized triangulenes, [4]helicenes and [6]helicenes in particular – the latter derivatives presenting helical geometries with very high barriers of racemization between enantiomers. The chemical, (chir)optical and photophysical properties are characterized and applied to questions in chemistry, biology and physics.
For recent or key references, see publications: 180, 176, 175, 171, 170, 167, 162, 161, 160, 154, 148, 145.
Metal Catalysis
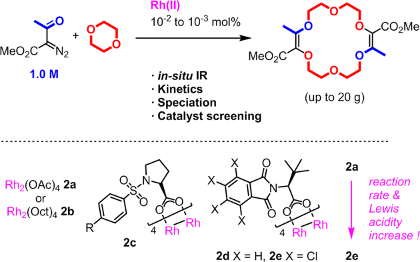
New transformations with high stereoselectivity, unprecedented outcome, interesting mechanisms or application potentials are developed.
More
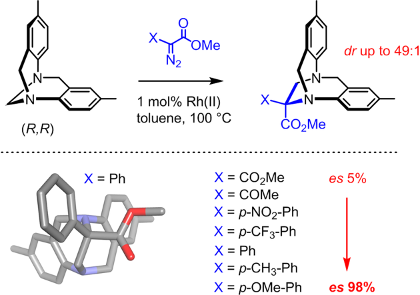
In relation with a previous topic, we use metal salts and complexes to catalyze the decomposition of diazo and triazole reagents. Based on detailed mechanistic studies, catalysts are designed for enhanced selectivity and reactivity. A particular emphasis is given to two different classes of complexes based of rhodium and ruthenium respectively that present, with the same substrates, an orthogonal reactivity. Many new transformations with high stereoselectivity, unprecedented outcome, interesting mechanisms or application potentials are developed.
For recent or key references, see publications: 179, 177, 169, 166, 159, 157, 152, 150, 146, 137, 136, 133, 130, 128, 127, 125, 124.
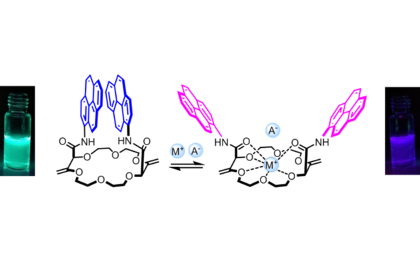
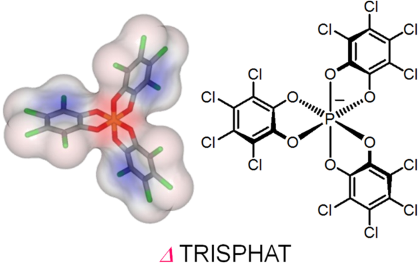
Ion-Mediated Chemistry
Our group studies processes involving ions and salts – and chiral anions in particular.
More
Our group strongly studies processes involving ions and salts. On one hand, the (chir)optical switching properties of ion-selective sensors are investigated. On the other hand, the synthesis and applications of octahedral hexacoordinated phosphorus anions. These compounds, such as TRISPHAT and BINPHAT are chiral by virtue of their three-bladed geometry (Δ and Λ enantiomers). TRISPHAT is usually efficient asymmetrically with cationic metallo-organic and organometallic substrates. BINPHAT has superior chiral solvating properties with more organic cations. These anions are efficient resolving agents and effective asymmetry-inducing agents.
For recent or key references, see publications: 174, 168, 166, 147, 140, 132, 131, 117 and references therein.