Publication 117
- Duplex formation and secondary structure of γ-PNA observed by NMR and CD
J. M. P. Viéville, S. Barluenga, N. Winssinger, M.-A. Delsuc
Biophys. Chem. 2016, 210, 9-13
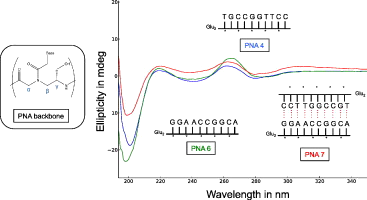
Peptide Nucleic Acids (PNA) are non-natural oligonucleotides mimics, wherein the phosphoribose backbone has been replaced by a peptidic moiety (N-(2-aminoethyl)glycine). This peptidic backbone lends itself to substitution and the γ-position has proven to yield oligomers with enhanced hybridization properties. γ-PNA backbone are formed by standard nucleic acids nucleobases connected by a neutral N-(2-aminoethyl)glycine backbone linked by a peptide bond. In this study, we use Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Circular Dichroism (CD) to explore the properties of the supramolecular duplexes formed by these species. We show that standard Watson-Crick base pair as well as non-standard ones are formed in solution. The duplexes thus formed present marked melting transition temperatures substantially higher than their nucleic acid homologs. Moreover, the presence of a chiral group on the γ-peptidic backbone increases further more this transition temperature, leading to very stable duplexes.
PNA duplexes with a chiral backbone present a marked chiral secondary structure, observed by CD, and showing a common folding pattern for all studied structures. Nevertheless small differences are observed depending on the details of the nucleobase sequence.
DOI : 10.1016/j.bpc.2015.09.002
archive ouverte unige:80855
