Publication 12
- Chiral Boron-Bridged Bisoxazoline (Borabox) Ligands: Structures and Reactivities of Pd and Cu Complexes
Valentin Köhler, Clément Mazet, Aurélie Toussaint, Klaus Kulicke, Daniel Häussinger, Markus Neuburger, Silvia Schaffner, Stefan Kaiser, Andreas Pfaltz*
Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 8530-8539
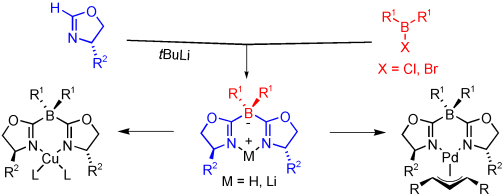
Anionic boron-bridged bisoxazolines (borabox ligands) have been synthesized and characterized in their protonated forms. The ligands are tuneable over a wide range, allowing either alkyl or aryl substituents at the oxazoline rings and the central bridging boron atom. The structural parameters of this new ligand type have been investigated by X-ray analyses of palladium and copper complexes. Electronic properties have been studied by 13C NMR spectroscopy and by DFT calculations on palladium allyl complexes and compared to those of analogous bisoxazoline (box) complexes. Borabox complexes are more electron-rich at the metal center than their neutral box congeners, and as a consequence of the longer bonds between the bridging atom and the oxazoline rings, their bite angles are larger. Palladium(II) complexes bearing an unsubstituted allyl ligand and homoleptic copper(II) complexes each possess an almost flat chelate ring. NMR analysis of a (1,3-diphenylallyl)(borabox)palladium complex showed a 92:8 mixture of (syn,syn) and (anti,syn) allyl isomers, in contrast with a previously reported box analogue that existed exclusively in the (syn,syn) form. Comparison of the corresponding crystal structures revealed that the distance between the bisoxazoline and the allyl ligand in the borabox complex is shorter. In the copper-catalyzed allylic oxidation of cyclohexene and cyclopentene with tert-butyl perbenzoate, borabox ligands gave results similar—and in some cases superior—to those obtained with analogous box ligands.
archive ouverte unige:7034
DOI de la version éditeur : 10.1002/chem.200800822
